In the world of sales, effective communication is the cornerstone of success. Whether you’re a seasoned sales pro or just starting your journey, understanding and speaking the language of sales is essential to connect with prospects, build relationships, and close deals.
But let’s face it, the sales landscape is riddled with jargon and specialized terminology that can be overwhelming.
That’s why we’ve created our comprehensive sales glossary, designed specifically for sellers like you. This invaluable resource will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to navigate sales conversations with ease, impress prospects, and elevate your selling game.
A strategic approach to sales that focuses on targeting and engaging specific high-value accounts with personalized and tailored messaging. It involves identifying key decision-makers within a target account, understanding their unique needs and challenges, and crafting customized solutions to address those needs. ABS aims to build strong relationships with individual accounts and deliver a personalized buying experience to drive higher conversion rates and revenue growth.
An account executive in sales is a professional responsible for managing and nurturing relationships with existing clients or prospective customers on behalf of a company. Their primary role is to drive sales by understanding the needs of clients, presenting products or services, negotiating contracts, and ensuring customer satisfaction.
Account executives typically serve as the main point of contact, working closely with clients to identify opportunities, address concerns, and provide ongoing support to maximize revenue and maintain long-term partnerships.
Annual Customer Value (ACV) is a metric used in business to calculate the average revenue or value generated by a customer over a one-year period. It takes into account factors such as recurring purchases, subscriptions, and contract renewals to determine the total value a customer brings to a company on an annual basis. ACV helps organizations assess the profitability and long-term worth of their customer relationships, allowing them to make informed decisions regarding customer acquisition, retention strategies, and resource allocation.
A Business Development Representative (BDR) is a sales professional responsible for prospecting, qualifying, and generating new business opportunities for a company. BDRs typically work closely with marketing and sales teams to identify potential leads, engage with prospects through various channels, and schedule meetings or demos for account executives or sales representatives. Their primary objective is to generate a pipeline of qualified leads and initiate the early stages of the sales process by nurturing relationships, conducting outreach, and gathering valuable market intelligence to support the company’s growth objectives.
B2B stands for “Business-to-Business” and refers to transactions, interactions, or relationships that occur between two or more businesses. It involves the exchange of products, services, or information between companies rather than between a business and individual consumers. B2B activities can include selling goods to other businesses, providing services, forming partnerships, or collaborating on projects. B2B transactions often involve larger quantities, specialized products or services, and negotiations tailored to the unique needs of the business customers involved.
B2C stands for “Business-to-Consumer” and refers to transactions, interactions, or relationships that occur between a business and individual consumers. It involves the sale of products, services, or information directly to end-users or customers for their personal use or consumption. B2C transactions typically occur through various channels such as online platforms, retail stores, or direct sales, and focus on meeting the specific needs and preferences of individual consumers. B2C businesses often employ marketing and advertising strategies to attract and engage with a wide range of consumers to drive sales and build customer loyalty.
BANT is an acronym commonly used in sales to qualify and assess potential leads or prospects. It stands for Budget, Authority, Need, and Timeline. Here’s a brief definition for each component:
- Budget: Refers to the financial resources or funding that a prospect has allocated or is willing to allocate for a particular product or solution.
- Authority: Indicates whether the prospect has the decision-making power or authority within their organization to make purchasing decisions.
- Need: Determines the specific pain points, challenges, or requirements that the prospect has, which the product or solution can address and fulfill.
- Timeline: Refers to the timeframe or urgency within which the prospect intends to implement or solve the identified need.
BANT serves as a framework for sales representatives to evaluate the viability of a lead, qualify them as a potential customer, and prioritize their efforts based on the prospect’s budget, decision-making authority, identified needs, and timeline for action
The Bottom of the Funnel (BOFU) represents the final stage in the buyer’s journey, where leads have progressed through the awareness and consideration stages and are now poised to make a purchasing decision. At this stage, prospects have a clear understanding of their problem, have evaluated various solutions, and are actively comparing options. Marketers and sales teams focus on providing detailed product information, addressing specific objections, and offering tailored solutions.
Tactics employed include personalized demos, free trials, case studies, pricing discussions, and contract negotiations. The primary goal is to convert qualified leads into customers by showcasing the value proposition, highlighting ROI, and addressing any remaining concerns, ultimately driving them toward a successful purchase.
Sales certification refers to a formal recognition or credential that validates an individual’s proficiency and expertise in sales-related knowledge and skills. It is typically offered by professional organizations, industry associations, or training institutions.
Sales certification programs assess and verify a sales professional’s understanding of sales concepts, techniques, best practices, and industry-specific knowledge. These programs often include comprehensive training, educational materials, assessments, and examinations to ensure that individuals meet the established standards for competence in the sales field. Sales certifications can cover a wide range of areas, such as consultative selling, sales management, relationship building, objection handling, negotiation, and ethical sales practices. Obtaining a sales certification demonstrates a commitment to professional development, enhances credibility, and may provide individuals with a competitive advantage in the job market or within their organizations.
Churn rate refers to the rate at which customers or subscribers discontinue or cancel their relationship with a company or cease using its products or services over a specific period. It is a key metric used to measure customer attrition or turnover and is typically expressed as a percentage. A high churn rate indicates a higher rate of customer loss, which can have negative implications for a company’s revenue and growth. Managing and reducing churn rate is an important focus for businesses as it impacts customer retention, profitability, and overall business success.
Closed rate, also known as the “closing rate” or “conversion rate,” is a sales metric that measures the percentage of successfully closed deals or sales opportunities out of the total number of qualified leads or opportunities. It represents the effectiveness of a sales team or individual in converting prospects into customers. A high closed rate indicates a higher success rate in closing deals, while a low closed rate may indicate areas for improvement in the sales process, such as lead qualification, objection handling, or negotiation skills. The closed rate is an essential metric for evaluating sales performance and optimizing sales strategies to maximize revenue and business growth.
In sales, “closed-won” refers to a status or outcome assigned to a sales opportunity when it has been successfully closed and resulted in a sale or a won deal. It signifies that a prospect has made the decision to purchase the product or service being offered, and all necessary agreements, negotiations, and contracts have been finalized. The closed-won status indicates a successful outcome for the salesperson or sales team, as they have successfully converted the opportunity into a customer and achieved their sales objective.
Conversation intelligence refers to the practice of capturing, analyzing, and deriving insights from sales and customer conversations. It involves leveraging advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence and natural language processing, to automatically transcribe and analyze conversations between sales representatives and prospects or customers.
Conversation intelligence platforms enable organizations to extract valuable data and insights from these interactions, such as key talking points, sentiment analysis, objection handling, and competitive intelligence. By applying conversation intelligence, sales teams can gain a deeper understanding of customer needs, improve sales effectiveness, and enhance coaching and training efforts. It serves as a powerful tool for optimizing sales strategies, improving customer interactions, and driving overall sales performance.
A Digital Sales Room, commonly referred to as a DSR, is a single platform for deal planning, communication, and content sharing. A digital sales room refers to a virtual or online platform where sales professionals can engage with potential customers, share information, and facilitate sales interactions in a digital environment. It serves as a centralized hub where sales representatives can showcase products or services, provide demonstrations, share presentations, and address customer inquiries or objections.
Digital sales rooms often leverage technology such as video conferencing, screen sharing, document sharing, and real-time messaging to create an interactive and immersive sales experience. These platforms enable sales teams to collaborate with prospects remotely, deliver personalized sales pitches, and guide customers through the sales process, replicating many aspects of a traditional face-to-face sales meeting. Digital sales rooms offer convenience, flexibility, and accessibility, allowing sales professionals to connect with customers from anywhere and at any time, improving efficiency and expanding sales opportunities in a digital sales environment.
A Front Line Manager, also known as a First-Line Manager or Supervisor, is an essential position within an organization responsible for overseeing a team of employees at the operational level. They are typically responsible for ensuring the smooth execution of day-to-day activities, managing workflow, and maintaining productivity within their department or team.
Front Line Managers play a vital role in implementing organizational policies and procedures, providing guidance and support to team members, monitoring performance, and addressing any issues or challenges that may arise. Their strong leadership skills, effective communication, and ability to motivate and develop their team contribute to the overall success and efficiency of the organization.
Field sales, also known as outside sales, refers to a sales approach where sales representatives or account executives meet and interact with prospects or customers in person, typically outside the office or at the client’s location. Instead of conducting sales remotely or through digital means, field sales professionals actively travel to meet with clients, conduct sales presentations, demonstrate products, negotiate deals, and build relationships face-to-face. Field sales is often employed in industries or situations where personal interaction, relationship-building, and customized sales approaches are essential for driving business growth and closing deals successfully.
A profile of a rep that’s likely to succeed at a given organization. Much like an ICP includes characteristics that make the customer “ideal,” an IRP defines the competencies and skills a rep must have to regularly close deals and meet (or even surpass) quota.
Learning that takes place where one or more educators, either virtually or in a classroom, teach skills through presentations, demonstrations, and discussions.
A lead in sales refers to an individual or business entity that has shown interest in a company’s products or services and has the potential to become a customer. It is typically a person or organization that has provided their contact information or engaged with the company through various channels, such as filling out a form, subscribing to a newsletter, attending an event, or expressing interest in a product demonstration. Leads are often considered as potential opportunities for sales teams to pursue and convert into paying customers through further engagement, nurturing, and the sales process.
Lead qualification is the process of assessing and evaluating potential leads or prospects to determine their suitability, readiness, and likelihood of becoming a customer. It involves gathering information, analyzing data, and applying specific criteria to determine whether a lead meets the requirements and characteristics of an ideal customer for a particular product or service. Lead qualification helps sales and marketing teams focus their efforts on leads that are most likely to convert, ensuring that resources and time are allocated effectively. It typically involves evaluating factors such as the lead’s budget, needs, timeline, decision-making authority, and fit with the company’s target market or buyer persona. The goal of lead qualification is to identify and prioritize high-quality leads that have the potential to drive successful sales outcomes.
Lead scoring is a methodology used in sales and marketing to assess and rank the quality or readiness of a lead based on predetermined criteria. It involves assigning numerical values or scores to leads based on factors such as demographic information, lead source, engagement level, behavior, and characteristics that indicate their likelihood of becoming a customer. Lead scoring helps prioritize and focus efforts on leads with higher potential or readiness, enabling sales and marketing teams to allocate resources effectively and prioritize follow-up activities. By using lead scoring, organizations can streamline their lead qualification process, improve lead-to-customer conversion rates, and optimize sales and marketing efforts.
A Learning Management System (LMS) is a software application or platform designed to facilitate the administration, delivery, and tracking of educational or training programs. It provides a centralized hub for managing and delivering various types of learning content, such as online courses, training modules, assessments, and resources. LMS platforms typically offer features such as user management, course enrollment, content creation and management, progress tracking, assessments, and reporting. They allow organizations, educational institutions, or trainers to create, organize, and deliver learning materials, track learner progress, and assess their performance.
LMS platforms can be used for a wide range of learning purposes, including employee training, professional development, compliance training, onboarding, and academic courses. They provide a scalable and efficient way to deliver and manage learning experiences, foster engagement and collaboration, and track the effectiveness of training initiatives.
Microlearning in sales training is an approach that delivers small, bite-sized units of targeted and focused learning content to sales professionals. It involves breaking down training materials into brief, easily consumable modules, typically ranging from a few minutes to 10-15 minutes in length. These modules are designed to address specific topics, skills, or knowledge gaps relevant to sales performance improvement.
Microlearning can take the form of short videos, quizzes, interactive exercises, or concise text-based lessons. By providing quick and easily accessible learning resources, microlearning allows sales professionals to engage in continuous learning and development on-demand, fitting into their busy schedules and facilitating knowledge retention and application.
MQL stands for Marketing Qualified Lead and refers to a lead or prospect that has been deemed as having a higher potential to become a customer based on their engagement with marketing efforts and meeting certain predefined criteria. MQLs are typically identified and qualified by the marketing team using a combination of factors such as specific actions taken by the lead (e.g., downloading a whitepaper, attending a webinar), their level of interest or engagement, and their fit with the target market or buyer persona. MQLs are then passed on to the sales team for further nurturing and conversion into customers through personalized sales efforts and follow-up activities.
The Middle of the Funnel (MOFU) refers to the second stage in the buyer’s journey, where potential customers have already shown interest in a product or service and are actively considering their options. At this stage, prospects are transitioning from the initial awareness stage to evaluating different solutions. Marketers and sales teams focus on nurturing leads, providing targeted and relevant information, and building trust and credibility.
MOFU involves tactics such as lead scoring, lead nurturing campaigns, personalized content, and engaging with prospects through channels like email, webinars, and demos. The goal is to educate and guide prospects toward making a purchase decision, ultimately moving them closer to becoming qualified opportunities for sales.
Net Promoter Score (NPS) is a widely used metric that measures the loyalty and satisfaction of customers towards a company or brand. It is based on a simple survey question: “On a scale of 0 to 10, how likely are you to recommend our company/brand/product/service to a friend or colleague?” Respondents are categorized into three groups: Promoters (score 9-10), Passives (score 7-8), and Detractors (score 0-6). The NPS is calculated by subtracting the percentage of Detractors from the percentage of Promoters, resulting in a score that ranges from -100 to +100.
A higher NPS indicates higher customer loyalty and advocacy, while a lower score suggests areas for improvement. The Net Promoter Score provides valuable insights into customer sentiment and can guide businesses in enhancing customer experience and driving growth.
A pain point refers to a specific problem, challenge, or frustration that a business or individual within a target company is experiencing. It is a source of dissatisfaction or unmet need that creates a sense of urgency or motivation for the business to seek a solution. Pain points can arise from various aspects of the company’s operations, such as inefficiencies, high costs, lack of productivity, compliance issues, or competitive disadvantages. Identifying and addressing these pain points is a critical aspect of B2B selling, as it allows sales professionals to position their products or services as a solution that can alleviate the customer’s pain and provide tangible benefits or improvements.
Prospecting in sales refers to the proactive and systematic process of identifying and qualifying potential leads or prospects who have the potential to become customers. It involves searching for and evaluating individuals or businesses that fit the company’s target market or buyer persona. Sales professionals engage in prospecting activities to initiate contact, gather relevant information, and assess the viability and potential value of the leads for the sales pipeline.
Prospectors may utilize various strategies and techniques, such as cold calling, email outreach, networking, social media research, and attending industry events, to identify and connect with potential prospects. The goal of prospecting is to generate a pool of qualified leads that can be further pursued and nurtured through the sales process with the aim of converting them into customers.
A qualified lead, also known as a sales-qualified lead (SQL), is a potential customer who has been assessed and determined to have a higher likelihood of converting into a sale based on predefined criteria. These criteria may include factors such as their level of interest, fit with the target market or buyer persona, budget, authority to make purchasing decisions, and specific needs or pain points that align with the company’s products or services. A qualified lead has shown a certain level of engagement and meets the necessary requirements to move forward in the sales process. Sales teams prioritize qualified leads for further nurturing and active sales efforts to convert them into customers.
A sales quota is a predetermined sales target or goal set for an individual salesperson or a sales team within a specific time period. It represents the desired level of sales performance that the individual or team is expected to achieve. Sales quotas are typically established based on factors such as revenue, units sold, profit margin, or other key performance indicators (KPIs) relevant to the organization’s sales objectives.
Quotas serve as a means to motivate and incentivize sales professionals, providing a clear benchmark for performance evaluation and measuring the success of sales efforts. Meeting or exceeding sales quotas is often tied to rewards, commissions, bonuses, or other forms of recognition within the sales compensation structure.
Revenue enablement refers to the strategic process of equipping sales teams and other revenue-generating functions within an organization with the necessary tools, resources, and support to maximize their effectiveness in driving revenue growth. It encompasses a range of activities aimed at empowering sales professionals to perform at their best and achieve their revenue targets.
Revenue enablement involves providing comprehensive training, access to relevant information and data, sales tools and technologies, streamlined processes, and effective collaboration between sales, marketing, and other departments. The goal of revenue enablement is to optimize sales productivity, improve customer engagement, and ultimately increase revenue generation across the organization.
Revenue intelligence refers to the practice of capturing, analyzing, and leveraging data and insights related to revenue-generating activities within an organization. It involves using advanced analytics, automation, and artificial intelligence (AI) technologies to gather and interpret data from various sources, such as customer interactions, sales pipelines, marketing campaigns, and financial systems.
Revenue intelligence provides a holistic view of the customer journey, sales performance, and revenue generation processes, enabling businesses to make data-driven decisions and optimize their revenue strategies. It helps organizations identify patterns, trends, and opportunities to improve sales effectiveness, customer engagement, and overall revenue growth. Revenue intelligence tools and platforms can provide valuable insights into customer preferences, buying behavior, market trends, and competitive landscapes, empowering businesses to align their sales and marketing efforts, improve forecasting accuracy, optimize pricing strategies, and drive revenue optimization across the organization.
Revenue productivity is a set of processes, strategies, and technologies used to enhance sales performance by utilizing seller data, revenue analytics, sales enablement, and front-line sales coaching.
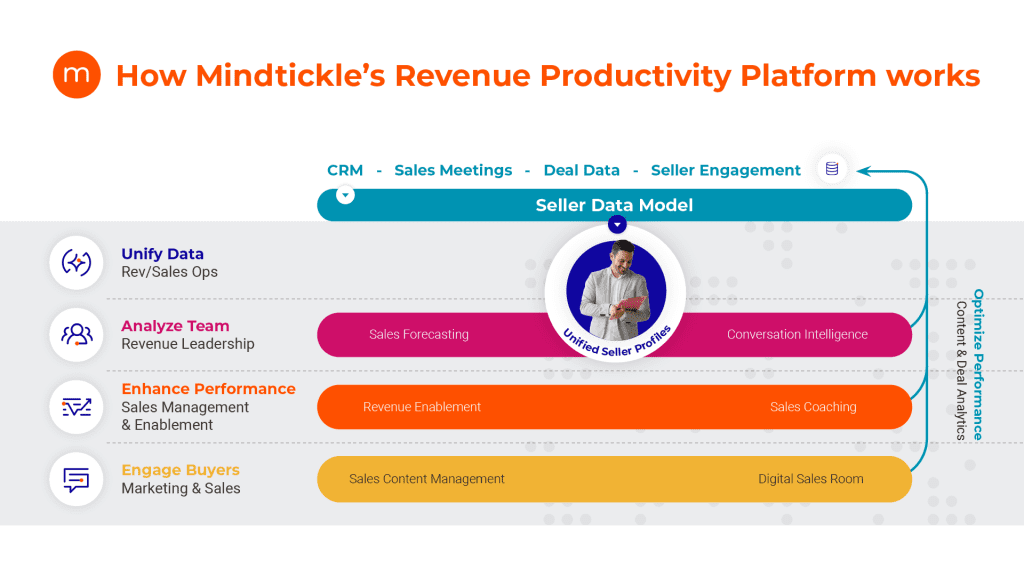
Revenue Operations, commonly known as RevOps, refers to the strategic alignment and integration of sales, marketing, and customer success operations within an organization. It focuses on optimizing revenue generation by streamlining processes, leveraging technology, and fostering collaboration across departments.
Revenue Operations brings together data, analytics, and insights to drive informed decision-making and improve overall operational efficiency. By breaking down silos and creating a unified approach to revenue management, RevOps aims to enhance customer experience, increase sales effectiveness, and maximize revenue growth. It serves as a bridge between different teams, aligning their goals and strategies to drive holistic revenue optimization and organizational success.
Sales coaching refers to the process of providing guidance, support, and feedback to sales professionals with the aim of improving their selling skills, performance, and overall effectiveness. Sales coaching involves a collaborative approach where a sales manager or experienced salesperson works closely with the sales representative to enhance their knowledge, abilities, and techniques in various aspects of the sales process. It may include activities such as role-playing, analyzing sales calls, reviewing sales metrics, offering constructive feedback, providing training on sales strategies, and setting performance goals.
The goal of sales coaching is to help sales professionals develop their strengths, overcome challenges, and achieve their sales targets by continuously improving their sales techniques, communication skills, relationship-building abilities, and overall sales effectiveness.
Sales content management refers to the strategic process of organizing, storing, and distributing sales-related content in a structured and efficient manner. It involves the systematic management of various types of content, including sales collateral, presentations, case studies, product information, and more. The primary goal of sales content management is to enable sales teams to easily access and utilize relevant and up-to-date content during customer interactions, thereby enhancing their effectiveness and improving the overall sales process. Effective sales content management ensures that sales representatives have the right information at their fingertips, empowering them to engage prospects, address their needs, and drive successful sales outcomes.
Sales enablement refers to the strategic approach of equipping sales teams with the resources, tools, and knowledge they need to effectively engage with prospects, close deals, and drive revenue. It involves the alignment of marketing, training, and sales efforts to enhance the overall sales process.
Sales enablement encompasses the development and delivery of training programs, creation of sales collateral and playbooks, provision of relevant and up-to-date product information, implementation of technology solutions, and ongoing coaching and support. By focusing on sales enablement, organizations empower their sales teams to deliver consistent messaging, address customer needs, overcome objections, and ultimately achieve their sales targets.
Sales onboarding refers to the process of integrating and orienting newly hired sales professionals into an organization, equipping them with the knowledge, skills, and resources necessary to succeed in their role. Sales onboarding typically involves training on product knowledge, sales techniques, company policies, and procedures, as well as providing access to tools and systems used in the sales process. The goal of sales onboarding is to accelerate the time it takes for new sales representatives to become productive and contribute to the organization’s sales goals.
Sales forecasting is the process of estimating or predicting future sales performance based on historical data, market trends, and other relevant factors. It involves analyzing past sales patterns, market conditions, customer behavior, and internal data to make informed projections about future sales revenue, unit sales, or customer acquisition. Sales forecasting helps businesses plan and make strategic decisions, such as budgeting, resource allocation, inventory management, and goal setting. It serves as a valuable tool for sales teams, executives, and stakeholders to anticipate and prepare for future sales outcomes and optimize business operations.
Sales force refers to the collective group of individuals within an organization who are responsible for selling its products or services. They are the front-line representatives of the company, engaging with customers, building relationships, and ultimately driving sales revenue. The sales force typically includes sales representatives, account managers, sales managers, and other supporting roles involved in the sales process. They are responsible for prospecting, qualifying leads, making sales presentations, negotiating deals, and maintaining ongoing customer relationships. The sales force plays a crucial role in driving business growth and achieving sales targets.
A Sales Kickoff (SKO) is an annual or periodic event held by an organization to energize, align, and equip its sales teams for success in the upcoming period. It serves as a launchpad to set sales goals, introduce new strategies, and foster team unity.
The Sales Kickoff brings together sales professionals, leaders, and executives to share insights, best practices, and industry trends. It typically includes engaging keynote speeches, workshops, training sessions, and team-building activities. The event aims to inspire and motivate sales teams, enhance their product knowledge, refine selling techniques, and strengthen collaboration, ultimately driving sales growth and fostering a positive sales culture within the organization.
Sales onboarding refers to the process of integrating and training new sales team members to equip them with the necessary knowledge, skills, and tools to succeed in their role. It involves providing comprehensive training and support during the initial stages of their employment to help them understand the company’s products or services, sales processes, target market, value proposition, and sales strategies.
Sales onboarding programs typically cover various aspects, including product training, sales methodologies, CRM usage, objection handling, and role-specific responsibilities. The goal of sales onboarding is to accelerate the ramp-up time of new sales hires, increase their productivity, and ensure they are equipped to effectively engage with prospects, close deals, and contribute to the overall sales goals of the organization.
Sales readiness refers to the state of preparedness and competency of sales teams to effectively engage with customers and close deals. It encompasses the knowledge, skills, and resources required for sales professionals to perform their roles successfully.
Sales readiness involves ongoing training, coaching, and enablement activities that ensure sales representatives have the necessary product knowledge, selling techniques, and understanding of the buyer’s journey. It also includes providing access to relevant sales tools, resources, and sales collateral. By focusing on sales readiness, organizations can equip their sales teams with the right capabilities to confidently engage with prospects, overcome challenges, and drive successful sales outcomes.
Sales training refers to the process of equipping sales professionals with the knowledge, skills, and tools necessary to effectively perform their sales roles. It involves structured learning activities and programs designed to enhance the sales team’s capabilities, improve their understanding of sales strategies and techniques, and strengthen their overall sales performance.
Sales training may cover various areas, including product knowledge, sales methodologies, prospecting, lead generation, effective communication and listening skills, negotiation tactics, objection handling, closing techniques, and customer relationship management. The training can be delivered through workshops, seminars, online courses, role-playing exercises, mentoring, and on-the-job training. The objective of sales training is to empower sales professionals with the necessary skills and confidence to build relationships, address customer needs, overcome challenges, and ultimately drive sales success for the organization.
“Top of the funnel” refers to the initial stage of the sales and marketing process, where potential customers are first introduced to a company, product, or service. It represents the broadest part of the customer acquisition journey, encompassing the awareness and lead generation phase. At the top of the funnel, the focus is on capturing the attention and interest of a large audience and turning them into leads or prospects. Various marketing tactics, such as content marketing, social media campaigns, advertising, and events, are employed to attract and engage potential customers. The goal at this stage is to generate a pool of qualified leads who can then be further nurtured and guided through the subsequent stages of the sales funnel.
Upselling is a sales technique where a seller encourages a customer to purchase a higher-priced or more advanced product or service than the one originally intended or considered. It involves offering additional features, upgrades, or premium options that enhance the customer’s experience or provide added value. The objective of upselling is to increase the overall purchase value and maximize revenue by convincing customers to opt for a higher-priced option that better meets their needs or desires. Effective upselling requires understanding the customer’s preferences, identifying opportunities where a higher-priced offering aligns with their interests, and presenting persuasive arguments to encourage the upgrade.
A value proposition refers to a concise and compelling statement that communicates the unique value and benefits that a product, service, or solution offers to a business customer. It outlines the specific reasons why a customer should choose a particular offering over competing alternatives. A value proposition in B2B sales typically addresses the key pain points, challenges, or goals of the target customer and highlights how the product or service can address those needs effectively. It emphasizes the value, differentiation, and competitive advantage that the offering brings to the customer’s business, such as increased efficiency, cost savings, improved productivity, or competitive edge. A strong value proposition is critical for capturing the attention of B2B buyers and differentiating oneself from competitors in the marketplace.
Sales velocity refers to the speed or rate at which sales opportunities move through the sales pipeline and result in closed deals. It is a metric that quantifies the efficiency and effectiveness of the sales process. Sales velocity takes into account factors such as the number of deals in progress, the average deal size, the win rate, and the length of the sales cycle. By measuring and analyzing sales velocity, organizations can gain insights into the overall health of their sales pipeline and identify areas for improvement. Increasing sales velocity can lead to faster revenue generation and improved sales performance.
Virtual sales training refers to the delivery of sales training programs and resources through online platforms and virtual technology rather than in-person settings. It allows sales professionals to access training content, interact with instructors, and participate in learning activities remotely, regardless of their geographical location.
Virtual sales training utilizes various tools and methods, such as webinars, virtual classrooms, video conferencing, online modules, interactive exercises, and assessments, to provide sales training and development opportunities. Participants can engage in real-time discussions, receive instruction and feedback, collaborate with peers, and access training materials conveniently from their own devices. Virtual sales training offers flexibility in terms of timing and accessibility, enabling sales teams to receive training without the constraints of travel or scheduling conflicts. It can be an effective and efficient way to enhance sales skills, knowledge, and performance in a remote or distributed sales environment.
Voice of the Customer (VoC) refers to the insights and feedback collected from customers to understand their preferences, needs, and expectations regarding products, services, and experiences. It involves actively listening to and capturing customer opinions, perceptions, and sentiments through various channels such as surveys, interviews, reviews, and social media.
The Voice of the Customer provides valuable qualitative and quantitative data that organizations can analyze to gain a deeper understanding of their target audience, identify areas for improvement, and make data-driven decisions. By incorporating the Voice of the Customer into their business strategies, companies can enhance customer satisfaction, loyalty, and retention, ultimately driving long-term success.
As the sales landscape evolves, new concepts and buzzwords emerge. Our sales glossary is regularly updated to reflect the latest trends and industry developments, ensuring that you stay up-to-date with the ever-changing sales landscape. Consider it your trusted companion for continuous learning and professional growth.
Want more guides and content to get you up to speed with all things sales enablement?







